Are Centrioles Present In Both Eukaryotic And Prokaryotic Cells?
TÓM TẮT
Prokaryotic Vs. Eukaryotic Cells (Updated)
Keywords searched by users: Are centrioles found in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells is centrosome present in eukaryotic cells, are centrioles present in plant cells, are centrioles found in plant or animal cells, centrosome animal or plant cell, cytoskeleton prokaryotic or eukaryotic, centrioles in eukaryotic cells, centriole function, is chloroplast prokaryotic or eukaryotic
Is Centriole Found In Both Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Cells?
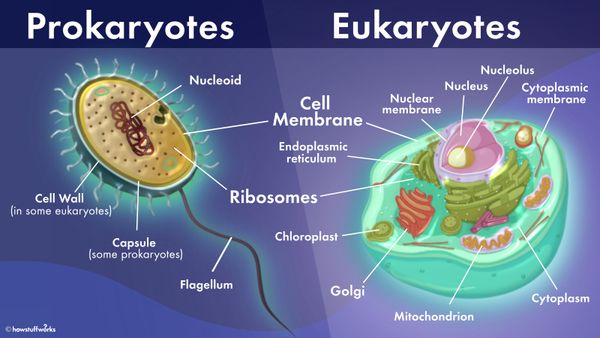
Do centrioles exist in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? The presence of centrioles, small cylindrical structures vital for cell division, varies between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. In prokaryotic cells, which lack a defined nucleus, genetic material is dispersed freely within the cytoplasm, and thus, centrioles are unnecessary during cell division. Consequently, prokaryotic cells do not possess centrioles. Conversely, eukaryotic cells, characterized by a true nucleus enclosed in a membrane, typically contain centrioles to facilitate the complex process of cell division.
Are Centrioles Found In Eukaryotic Cells?
Centrioles, crucial cellular structures, are commonly found in a wide range of eukaryotic cells. However, it’s important to note that they are notably absent in certain organisms, such as conifers (Pinophyta), flowering plants (angiosperms), and most fungi. In these particular species, centrioles are not a part of their cellular architecture. Interestingly, centrioles are present in a specialized manner, specifically within the male gametes, in several other plant groups including charophytes, bryophytes, seedless vascular plants, cycads, and Ginkgo. This distribution highlights the diversity in centriole occurrence across the plant kingdom, with some groups having them widely and others displaying a more limited presence.
Where Are Centrioles Found In Eukaryotic Cells?
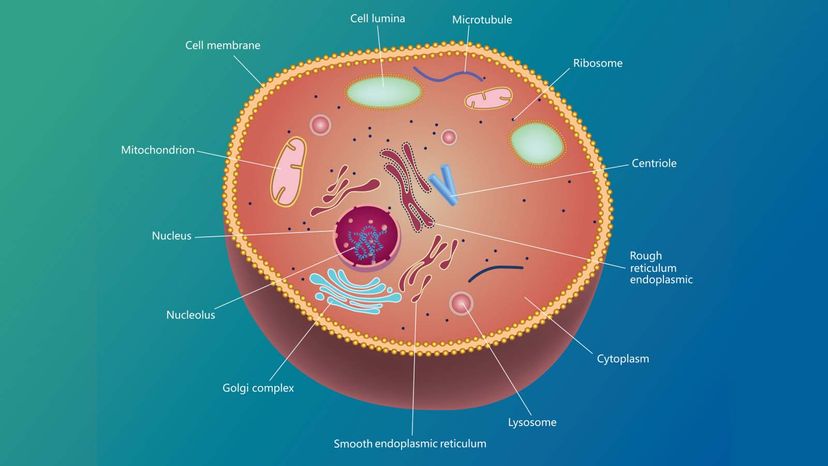
Centrioles, essential organelles in eukaryotic cells, are typically found as a pair of barrel-shaped structures situated within the cytoplasm of animal cells, positioned near the nuclear envelope. Their primary function revolves around orchestrating the organization of microtubules, which act as the cell’s internal structural framework. These microtubules serve various crucial roles, such as aiding in cell division, facilitating intracellular transport, and maintaining cell shape. By coordinating the formation and arrangement of microtubules, centrioles contribute significantly to the overall functionality and structure of the cell.
Summary 25 Are centrioles found in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/animal-cells-vs-plant-cells-373375_final-5b462d7fc9e77c00375014f1.png)


Categories: Discover 39 Are Centrioles Found In Eukaryotic And Prokaryotic Cells
See more here: buoitutrung.com

Prokaryotes do not have centrioles. Only eukaryotic cells have centrioles. Centrioles make up the centrosome, which is important for organizing spindle fibers during cell division in eukaryotes.In a prokaryotic cell, genetic material flows freely in the cytoplasm. So there is no need for centriole during cell division. Hence prokaryotic cell doesn’t have centriole.Centrioles are found in most eukaryotic cells, but are not present in conifers (Pinophyta), flowering plants (angiosperms) and most fungi, and are only present in the male gametes of charophytes, bryophytes, seedless vascular plants, cycads, and Ginkgo.
Learn more about the topic Are centrioles found in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.
- Do prokaryotes have centrioles? – Homework.Study.com
- Are centrioles found in prokaryotic cells? – BYJU’S
- Centriole – Wikipedia
- Centriole – National Human Genome Research Institute
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells | CK-12 Foundation
- Animal Cell Structure – Centrioles – Molecular Expressions Cell Biology
See more: blog https://baannapleangthai.com/tech
